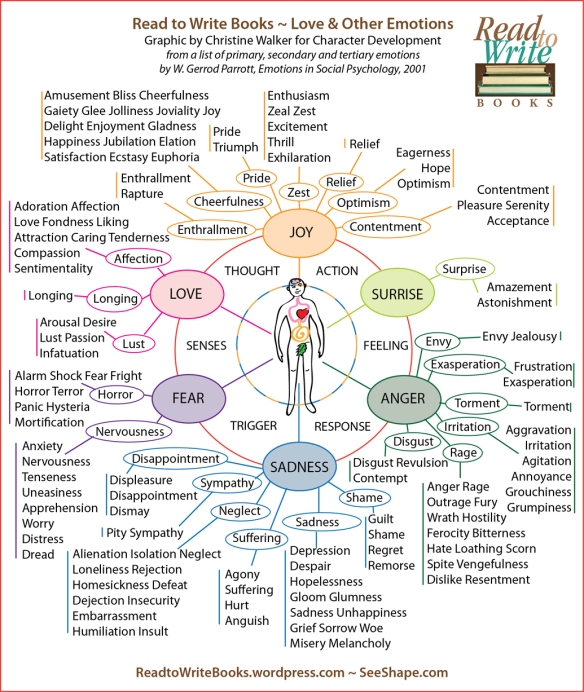
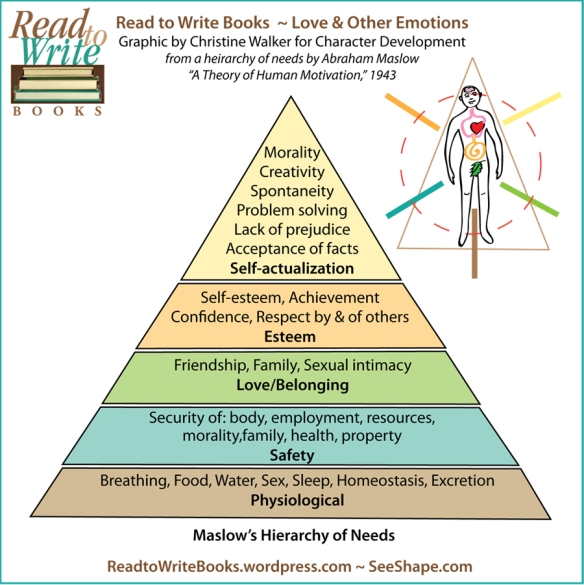
Would you like to create a more vivid presence of place in your fiction? Here’s a Moment of Mastery to inspire your creative process for success: Name the flora and fauna.
A subscriber to my YouTube channel suggested that I feature award-winning mystery writer James Lee Burke for this topic. His descriptive prose gives place a compelling presence while serving the story. Watch the video and/or read below.
In “Black Cherry Blues,” Burke’s naming of flora and fauna stimulates the senses and sets up character: “It was a place of salt-poisoned grass, alligators, insects, magpies, turkey buzzards, drowned cows whose odor reached a half mile into the sky, tropical storms that could sand the paint off a water tower, and people like my friend who had decided to slip through a hole in the dimension and live on their own terms.”
Burke describes a world so uninviting that even before you meet the friend, you already know something about him. Who could tolerate living in this hostile place?
In “A Morning for Flamingos,” the insistent naming of plants creates a felt, human-scale space and movement through it: “My apartment was inside a walled courtyard that you entered through an iron gate and a domed brick walkway. The flower beds were thick with blooming azalea and camellia and untrimmed banana tress, and the people who lived in the second-story apartments had placed coffee cans of begonias and hung baskets of impatiens along the balcony.”
The reader looks up. In spite of the security assumed by the iron gate, the hanging plants suggest unease and add to the story’s tension.
In “Dixie City Jam,” the naming of one specific bird and plant creates a sharp-focused scene: “Down below in the muddy current, a dead snow egret floated among an island of twigs and torn camellia leaves. The egret’s wing had been broken, and above one eye was the coppery glint of an embedded BB in the feathers.” The dead bird contrasts the stark beauty of life with death.
In “Heaven’s Prisoners,” a listing of views in rapid succession creates cinematic space: “The sugar cane and rice fields were behind me now. The black earth and flooded cypress and oak trees were replaced by pastureland and piney woods, lumber mills and cotton acreage, sandy red roads that cut through the limitless pecan orchards.”
The landscape speeding by serves the story with a sense of distance and time passing.
What places do you know well? Where have you lived and visited that shaped who you are? From that knowing can come powerful presence of place for your writing. Or do research. When populating place, put in specific flora and fauna to develop character, create tension, add sensory detail, and serve the story in many ways.
WRITING PROMPT: Think of a place or look at the photo of the alley in the video. Begin a scene. Add flora and fauna. Name them. Not just a hanging plant, but a genus or species – a Japanese wisteria or Million Bells. Not just an alley cat, but a breed – a Sphynx or Savannah. See how the names enhance and suggest more for the scene and start a story.
For a free trial of my online course “Writing Fiction: 9 Ways to Mastery” go to courses.christinewalker.net
Visit my YouTube channel for videos on writing fiction, memoir, visual storytelling, and creative process. Transform Your Story —the one you’re writing, the one you’re living.